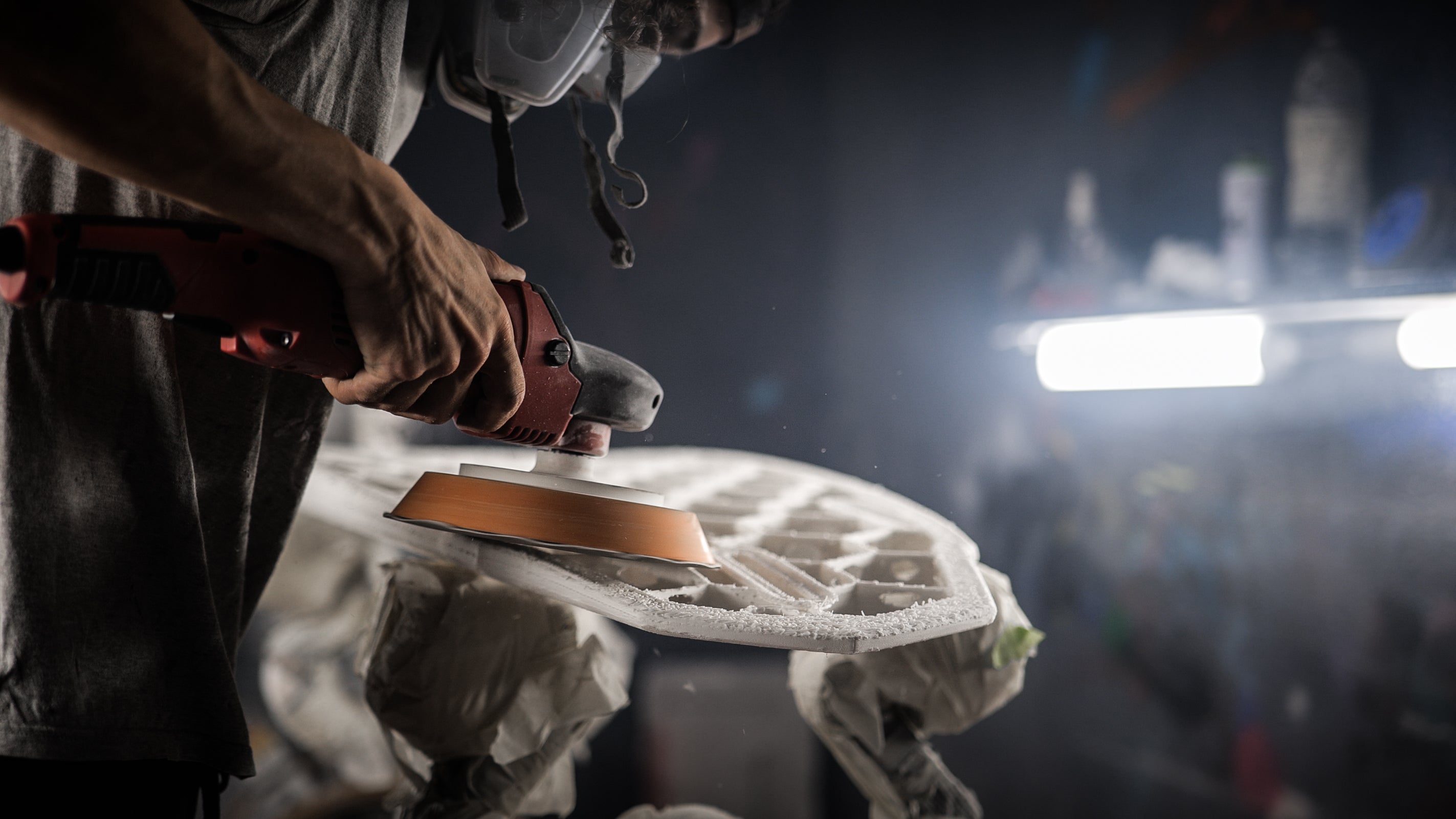
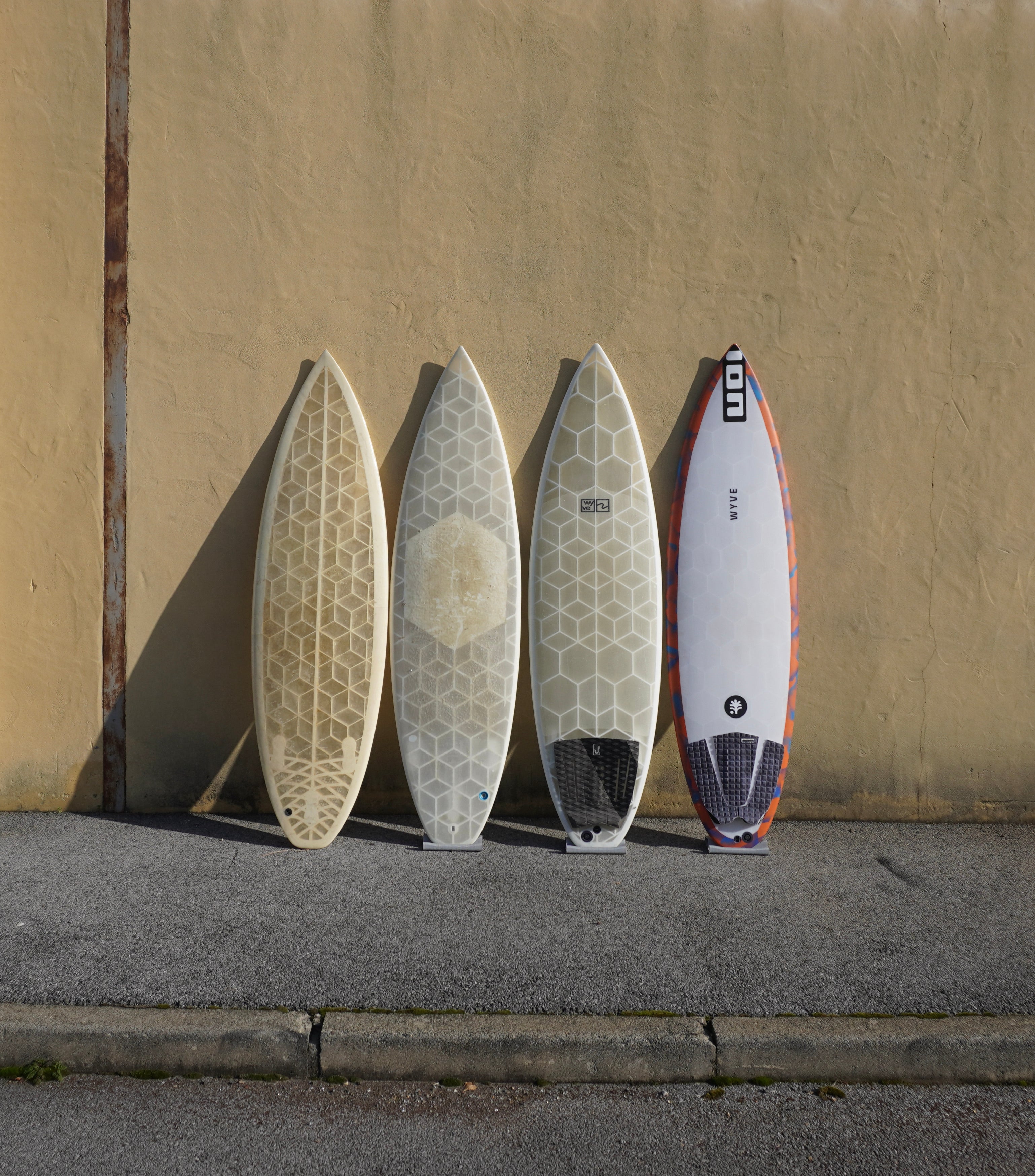
Embark on an exhilarating exploration of surfboard construction! While surfboards may appear as works of art with their sleek designs and waxed finishes, there's a fascinating world of high-tech materials hidden beneath the surface. In this in-depth journey, we'll peel back the layers that constitute a surfboard and delve into the groundbreaking innovations driven by materials like polyurethane foam, epoxy resin, and fiberglass cloth.
Whether you're a seasoned surf aficionado or simply intrigued by the science behind these aquatic crafts, our deep dive promises to unveil the hydrodynamic wizardry that goes into creating surfboards.
From the early days of solid wood planks to the modern shortboard revolution, we'll trace the evolution of surfboard materials and their impact on performance and maneuverability.
Join us in celebrating the marriage of technology and tradition that has shaped the surfboards we know and love today.

Key Takeaways:
-
Surfboards have evolved significantly over the years, thanks to high-tech materials like polyurethane foam, epoxy resin, and fiberglass cloth.
-
Polyurethane (PU) foam is the traditional core material for surfboards. It provides a smooth and responsive feel, making it a favorite among surfers for its timeless qualities.
-
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam is a lighter alternative, offering easier paddling and design flexibility. It is often paired with epoxy resin and suits specific wave conditions.
-
The outer shell of a surfboard consists of layers of fiberglass cloth and resin. Different types of fiberglass and resin combinations impact flexibility, strength, and performance.
-
Special materials like carbon fiber, wood veneer, and impact foams are used to enhance surfboard construction for various purposes.
-
Choosing the right materials for your surfboard depends on factors like your skill level, wave size, surf style, and environmental concerns.
-
Surfboards can now be 3D printed, allowing for precise customization and unique design possibilities.
In summary, understanding the materials used in surfboard construction is essential for selecting the right board that suits your surfing needs and preferences. Whether you prefer the classic feel of polyurethane or the lightweight versatility of EPS, there's a perfect board out there for you.
A Brief History of Surfboard Materials
Before the 1950s, surfboards were solid wood planks that required great skill but limited maneuverability. Then along came polyurethane foam and fiberglass. These space-age materials enabled new board shapes and kicked off a "shortboard revolution" still felt today.
Early surfboard makers like Hobie Alter and Gordon "Grubby" Clark pioneered techniques for laminating glass cloth and polyester resin over foam cores. Clark's invention of the foam-filled "Grubby Clark" fin provided another leap. Such innovations opened the floodgates for radical experiments in board design.
By the 1990s, epoxy resin and newer foam types added even more advances. Surfboard craft continues to evolve, but polyurethane, epoxy, fiberglass, and foam have become irreplaceable cornerstones.
The Core: Surfboard Foam Types
At a surfboard's heart lies its foam core. Polyurethane and polystyrene foams each have benefits depending on the board's desired qualities.
Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane (PU) foam dominates traditional surfboard construction. The dense material withstands pressure changes and resists dings. It creates lightweight boards with a smooth, responsive feel.
PU's flexibility lends to feedback through the curves. This tunes surfers into the wave's nuances. PU also excels at cutting through turbulence and handling chop.
Downsides of polyurethane include lower durability and difficult repairs. Costs run higher too for hand-shaped boards. Still, polyurethane delivers that timeless "surfy" experience generations have cherished.
Expanded Polystyrene Foam
For surfboards with incredible lightness and an extra pop, expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam fits the bill. At around half the density of PU, it floats higher on the waterline for easier paddling.
EPS construction first surfaced in the 1950s but wasn't widespread until recently. EPS introduces design possibilities like thinner rails while retaining strength. Its rigidity, however, reduces nuanced feedback.
Repairs are easier with EPS thanks to epoxy resins. Air pockets within the closed-cell foam improve buoyancy. EPS makes an exceptional choice for small, hollow waves where a lively feel helps.
The Shell: Fiberglass and Resin Lamination
Fiberglass cloth and resin provide the exterior shell over a surfboard's foam core. They create a seamless, liquid-tight barrier that's durable and responsive.
Fiberglass Cloth Types
Not all fiberglass is equal. Variations in the weave pattern and number of layers used impact flex and performance. Some top cloth types include:
- Standard Weave Fiberglass: The go-to choice for a nice balance of flex and strength. Its tight weave prevents excess resin absorption.
- S-Glass: Low resin absorption makes S-glass ideal for glossy finishes. It has excellent strength-to-weight ratios along with impact resistance.
- Vectorply Cloth: Uses a biaxial weave with fibers oriented along two 0/90 degree axes. Enhances torsional stiffness.
- Carbon Fiber: Woven carbon strands add tremendous rigidity and pop. Often used with fiberglass for a performance hybrid effect.
Resin Options
Whether coating a PU or EPS core, resin seals and protects the exterior laminate layers. Polyester and epoxy are the most common:
- Polyester Resin: The cheaper option at the cost of lower durability. Easy for do-it-yourself board builders. Requires more care to prevent yellowing and hazing.
- Epoxy Resin: Used with EPS and carbon boards. More eco-friendly yet expensive. Difficult for hand-shaping. Provides incredible transparency, durability, and gloss when hardened.
Proper resin curing eliminates bubbles between laminate layers. Surfboard makers carefully regulate temperature and hardening times to maximize quality.
Advanced Materials: Carbon, Wood Veneer and More
Beyond the classic triad of foam, fiberglass and resin, builders add special touches with advanced materials:
- Carbon Fiber: Woven carbon fiber sheets boost stiffness and liveliness. They complement fiberglass for a hybrid effect.
- Wood Veneer: Thin wood layers like bamboo add aesthetics and damping. An eco-friendly alternative to full wood boards.
- Reinforced Composites: Fabrics like Vectorply increase torsional stiffness to augment turning response.
- Impact Foams: High-density impact foam packs extra durability into high-wear areas. Protects from injury against rails or fins.
The Right Stuff: Choosing Your Surfboard Materials
With endless combinations to choose from, how do you select the right construction materials for your surfboard?
- Skill Level: Beginners fare best with soft-top boards before advancing to epoxy or PU/fiberglass. Shortboards use stiffer composites than longboards.
- Wave Size: Larger waves demand durable but lively PU or carbon. Smaller waves shine with ultra-buoyant EPS.
- Surf Style: More traditional riding feels best with PU polyester builds. Futuristic tricks need EPS, epoxy and carbon pop.
- Environmental Impact: EPS epoxy has a smaller footprint than PU fiberglass. Wood veneers are also eco-friendly touches.
By mapping your goals to material strengths, you can find the ideal makeup for maximum surfing enjoyment. Don't be afraid to demo boards and experiment on your quest for the perfect ride.
Conclusion,
Surfboards are not just iconic slices of fiberglass; they are the result of a harmonious blend of artistry and high-tech materials designed for optimal performance and durability.
Our exploration has taken us through the evolution of surfboard materials, from the days of solid wood planks to the transformative introduction of polyurethane foam and fiberglass. This shift paved the way for the shortboard revolution, forever changing the landscape of surfing.
At the heart of every surfboard is the choice of foam material, with polyurethane foam providing a timeless, responsive feel and expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam offering buoyancy and versatility. The exterior shell, crafted from fiberglass cloth and resin, ensures strength and responsiveness, with various options like S-glass and carbon fiber imparting distinct flex and performance characteristics.
Resin choices, including polyester and epoxy, play a pivotal role in sealing and protecting the exterior layers, with epoxy standing out for its eco-friendliness and superior properties. Advanced materials such as carbon fiber, wood veneer, and impact foams bring specialized enhancements to surfboard construction, catering to different riding styles and needs.
Selecting the right materials for your surfboard depends on factors like skill level, wave size, surf style, and environmental considerations. With an array of material combinations available, aligning your goals with material strengths is key to finding the perfect board for your surfing adventures.
The surfboard industry continues to push boundaries, with the advent of 3D printing technology offering unparalleled customization and design possibilities. Armed with a deep understanding of surfboard materials and construction techniques, you are now well-prepared to embark on your surfing journey with a newfound appreciation for the craftsmanship behind these aquatic crafts.
Whether you opt for the classic feel of polyurethane or embrace the lightweight versatility of EPS, remember that the true magic of surfing happens when you have your dream board beneath your feet. So, seize the opportunity, catch the waves, and live the surf life to the fullest!
FAQ
What material are surfboards made from?
Surfboards are primarily made from foam, commonly referred to as the "core" material. This foam core is then covered with layers of fiberglass and resin to create a strong and lightweight structure.
Do surfboards have fiberglass?
Yes, surfboards have fiberglass. Fiberglass cloth is an integral part of surfboard construction. It is applied to the foam core and saturated with resin to provide strength, rigidity, and durability to the board.
What are solid surfboards made of?
Solid surfboards, also known as "wooden" or "timber" surfboards, are traditionally made from solid wood. These boards are hand-shaped from a single piece of wood, such as balsa or paulownia. However, modern solid surfboards may also incorporate foam cores with a wooden veneer for added strength and performance.
Are all surfboards made of foam?
While the majority of surfboards feature a foam core, there are exceptions. Solid wooden surfboards, as mentioned earlier, do not have a foam core. Additionally, some specialized surfboards, like hollow wooden boards, may have unique constructions that differ from the foam core design as well 3D-Printed Surfboard.
Are there surfboards made with 3D printing technology?
Yes, some surfboards are now made using 3D printing technology. This innovative approach allows for precise customization and unique design possibilities, further expanding the options available to surfers.
This addition highlights the use of 3D printing technology in surfboard manufacturing, offering a modern and customizable alternative to traditional construction methods. If you have any more questions or need further information, please feel free to ask.